SD HD 4K
When you are watching videos on a bigger screen compared to a tablet or phone screen the differences between the four most common video qualities become apparent. Lets have a look at the differences between SD, HD and 4K.
SD
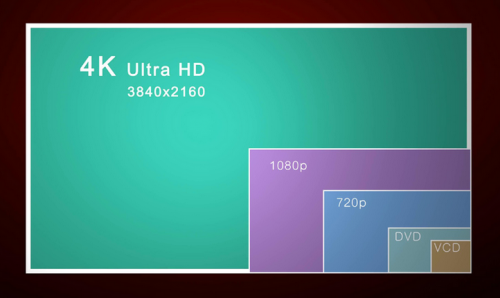
SD is the abbreviation of Standard Definition. As the name already suggests, it was the standard quality of movies and other videos for a long time. SD has a physical resolution below 720p (1280x720) format.
The resolution of SD has long been measured using the vertical resolution of lines. In South and North America as well as some other countries like Japan, the typical resolution of SD is 480i (also referred to as 480p). In Europe, Africa, Australia and most of Asia, however, the resolution is 576i.
When watching videos on a smaller screen (like a tablet or smartphone) the difference between other formats may not be striking. On a TV or bigger computer screen, however, an SD video appears in low quality.
HD
HQ stands for High Quality. Contrary to the other qualities, when talking about a HQ movie, the screen resolution and thus the pixels per line do not play a role. High quality videos are defined by an increased bitrate which leads to an overall better quality of the pictures shown.
So now to HD the most commonly known quality or screen resolution when talking about movies nowadays. It stands for High Definition” and the resolution is far better and higher than of SD videos. HD videos have a bigger file size when stored and require longer loading times when watching or streaming.
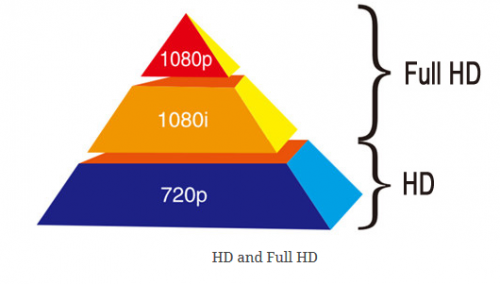
The typical resolutions are 720p and 1080p (also called full HD).
4K
Ultra high definition also known as UHD/4K this standard includes 4K UHD and 8K UHD. 4K UHD reaches approximate 8.29 megapixels resolution (3840x2160), while 8K UHD reaches approximate 33.18 megapixels (7680x4320) and to provide smooth and low bit-rate video streaming, Ultra high definition devices adopt the latest H.265/HEVC compression format. Compared with H.264, the latest H.265 can improve compression efficiency and H.266 is on it's way.